Jumat, 31 Desember 2010
Rabu, 29 Desember 2010
CCNA Discovery 4 Module 4 Exam Answers Version 4.0
• final project costs
• maintenance costs
• user satisfaction
• statistics describing the performance of network devices
2. Which two network applications are most affected by network congestion and delays? (Choose two.)
• IP telephony
• live video webcasts
• audio file downloads
• online banking services
• file archival and retrieval
3. What two Cisco tools can be used to analyze network application traffic? (Choose two.)
• NBAR
• NetFlow
• AutoQoS
• Wireshark
• Custom Queuing
4. In network design, which technology can be implemented to prioritize traffic based on its importance and technical requirements?
• STP
• QoS
• RTP
• TCP
• VPN
5. What are two characteristics of voice over IP traffic? (Choose two.)
• Voice packets tend to be small.
• Voice packets must be processed in real time.
• Voice packets can effectively use TCP reliability features.
• Voice traffic can survive packet drops and retransmission delays.
• Voice packets must be converted to analog before being sent across the IP network.
• Voice packets automatically receive a higher priority value than other types of packets.
6. What are two things that a network designer can do to determine current and anticipated network traffic flows? (Choose two.)
• Survey end users to obtain customer input.
• Upgrade the Cisco IOS software in all networking devices to optimize traffic flow.
• Limit the analysis to host-to-server traffic because host-to-host traffic is unimportant.
• Run a network traffic analysis to determine which applications are in use and by whom.
• Conduct an inventory of all networking devices that includes model numbers and memory configurations
7. A company that has a traditional telephone system wants to convert to IP telephony. Which two factors should be considered for the design? (Choose two.)
• Digital communications systems have greater noise than analog systems when processing voice traffic.
• Voice-enabled routers or a server must be used for call control and signaling.
• Voice to IP conversions can cause router overhead.
• Power to the phones can be supplied through properly equipped patch panels or switches.
• The cost to combine voice and data VLANs can be a considerable amount.
8. Several web and email servers have recently been installed as part of an enterprise network. The security administrator has been asked to provide a summary of security features that can be implemented to help prevent unauthorized traffic from being sent into or out of sensitive internal networks. Which three features should the security administrator recommend? (Choose three.)
• firewalls
• priority queuing
• access control lists
• intrusion detection systems
• DHCP
• 128-bit WEP
9. The design of an IP telephony system needs to meet the technical requirements to provide a connection to the PSTN as well as provide high-quality voice transmissions using the campus network. Which two elements directly affect the ability of the design to meet these requirements?(Choose two.)
• voice-enabled firewall
• PoE switches and patch panels
• redundant backbone connectivity
• voice-enabled router at the enterprise edge
• separate voice and data VLANs with QoS implemented
10. When implementing VoIP services, which two design considerations should be followed?(Choose two.)
• Confirm that network jitter is minimal.
• Use TCP to reduce delays and dropped packets.
• Establish priority queuing to ensure that large data packets are sent uninterrupted.
• Disable real-time protocols to reduce queuing strategy demands.
• Ensure that packet delays do not exceed 150 ms.
11. What design strategy should be followed when designing a network that uses video on demand?
• implement the appropriate routing protocol to ensure that data segments arrive in order
• implement different QoS queues based on the type of video traffic being distributed
• install servers to store the data in a centrally located server farm
• configure queuing in the core routers to ensure high availability
12. When implementing QoS in traffic queues, what is the first step the designer should take to ensure that traffic is properly prioritized?
• define QoS policies
• define traffic classes
• determine traffic patterns
• identify traffic requirements
• identify networking equipment
13. Which two statements are characteristics of file transfer traffic flows? (Choose two.)
• RTP should be used.
• Traffic is predictable.
• Packets are small in size.
• Transfers are throughput intensive.
• Response-time requirements are low.
14. Which two items can be determined by diagramming internal traffic flow? (Choose two.)
• the type of ISP services needed
• the capabilities of end-user devices
• the areas where network congestion may occur
• the location of VPN servers used to connect teleworkers
• locations where high-bandwidth connections are required
15. Which two traffic types are examples of external traffic flows? (Choose two.)
• A user in the IT department telnets to the core layer router.
• A user in marketing connects to the web server of a competitor.
• A user in the IT department telnets into the access layer switch.
• A user in the services department logs in to a web-based email program.
• A user in accounting connects to an FTP server that is connected to the access layer switch.
16. Which service can be provided by the NetFlow Cisco utility?
• network planning and mapping
• IDS and IPS capabilities
• peak usage times and traffic routing
• network billing and accounting application
• security and user account restrictions
• source and destination UDP port mapping
17. Refer to the exhibit. If ACL 150 identifies only voice traffic from network 192.168.10.0/24 and no other traffic, which queue will voice traffic from other networks use?
• high
• normal
• medium
• default
18. Refer to the exhibit. After configuring QoS, a network administrator issues the command show queueing interface s0/1. What two pieces of information can an administrator learn from the output of this command? (Choose two.)
• queue traffic definitions
• priority list protocol assignments
• type of queuing being implemented
• number of packets placed in each queue
• queuing defaults that have been changed
• queuing has not been applied to this interface
19. An analysis of network protocols reveals that RTP and RTCP are being used. What uses these protocols?
• IDS
• VPN
• WLAN
• firewall
• real-time video
20. A company is considering adding voice and video to the data networks. Which two statements are true if voice and video are added? (Choose two.)
• PoE switches must be purchased.
• More UDP-based traffic flows will be evident.
• Response times will be increased even if QoS is implemented.
• QoS will most likely be implemented to prioritize traffic flows.
• VPNs will most likely be implemented to protect the voice traffic.
21. Refer to the exhibit. Which option correctly matches the terms on top with its definition on the bottom?
• A=1, B=3, C=2, D=4
• A=2, B=1, C=4, D=3
• A=2, B=4, C=1, D=3
• A=3, B=2, C=4, D=1
• A=4, B=3, C=1, D=2
• A=4, B=2, C=3, D=1
22. A database server is configured to purge all data that is 60 days old. Ten data items that are 60 days old are to be purged. However, there is a failure halfway through the transaction, and the entire transaction is voided. What type of transaction action occurred?
• atomic
• consistent
• durable
• isolated
23. What is the primary goal of QoS?
• classification of traffic
• filtering and queuing voice traffic
• reducing bandwidth requirements
• providing priority service to selected traffic
24. Which technology provides a mechanism for implementing QoS at Layer 2?
• ToS
• CoS
• DSCP
• IP precedence
25. A customer purchases tickets online and pays using a credit card, but the system goes down before the transaction is complete. What transaction type retains a record of this transaction after the system failure so that the customer will still receive the tickets and the credit card account will be debited accordingly?
• atomic
• consistent
• durable
• isolated
26. Refer to the exhibit. The network design documents include requirements to prevent switching loops, to provide link-specific failover, and to provide Layer 3 recovery. Which two protocols would be needed to provide the support? (Choose two.)
• HDLC
• HSRP
• PPP
• RSTP
• VTP
27. network design must minimize latency to support real-time streaming applications. Which two protocols enable control and scalability of the network resources and minimize latency by incorporating QoS mechanisms? (Choose two.)
• RTCP
• HSRP
• RSTP
• RTP
• RPC
28. Which two major differences are associated with IP telephony when compared to traditional telephony that uses a PBX? (Choose two.)
• manages phones centrally
• utilizes centralized call routing
• creates peer-to-peer relationships between phones
• requires a separate infrastructure to support data transfer
• requires significant manual configuration when adding, moving, or changing phones
29. When QoS is implemented in a converged network, which two factors can be controlled to improve performance? (Choose two.)
• link speed
• delay
• packet routing
• jitter
• packet addressing
CCNA Discovery 4 Module 2 Exam Answers Version 4.0
• Prepare Phase
• Plan Phase
• Design Phase
• Implement Phase
• Operate Phase
• Optimize Phase
2. Which stage of the Cisco Lifecycle Services strategy is usually completed before an organization issues a Request For Proposal (RFP) or Request For Quotation (RFQ)?
• Prepare Phase
• Plan Phase
• Design Phase
• Implement Phase
• Operate Phase
• Optimize Phase
3. What is the purpose of SNMP?
• to facilitate the exchange of information between devices and the NMS
• to monitor and control managed network devices
• to report user logins to a monitoring station
• to verify traffic throughout the network and keep a log of all activity
4. During an analysis of a customer network, several possible opportunities for network improvement are identified. At which stage of the Cisco Lifecycle Services does this process occur?
• Prepare Phase
• Plan Phase
• Design Phase
• Implement Phase
• Optimize Phase
• Operate Phase
5. What provides the initial data for the Optimize Phase?
• performance monitoring
• business goals
• technical goals
• RFP
6. Which two statements are true regarding the response to an RFQ?(Choose two.)
• The response should be brief.
• it should strictly conform to the formatting requirements specified by the RFQ.
• Only the items that the contracting company will be addressing should be answered.
• The response helps the customer compare pricing with other potential contractors.
• The response is more complicated than a response to a RFP.
7. What are two disadvantages of using a bottom-up approach instead of a top-down approach to network design? (Choose two.)
• It can result in an inappropriate network design.
• A new design cannot be implemented right away.
• It does not take into account the business goals of the company.
• This approach is not commonly practiced and is therefore not as well known.
• It requires tedious and time-consuming meetings with the customer to develop an understanding of the organization.
8. What is a business constraint that may impact the WAN design of a company?
• company policy regarding specific operating systems on LAN devices
• current monitoring protocols implemented on end-user devices
• non-availability of end users during implementation
• company policy requiring the use of specific vendor networking equipment due to partnerships
9. What is the purpose of preparing a business case?
• to justify the financial investment in implementing the technology change
• to provide an example of a previous job done in the RFP
• to define the technical requirements of the network
• to define timelines and critical milestones
10. What is the purpose of creating a prioritized list of technical requirements?
• defines the project scope
• determines the business profitability
• creates a feasibility report for analysis
• identifies existing and new user groups
11. A network engineer is analyzing the network of a potential client company to identify problems and determine whether a network upgrade or addition is needed. Which role in the sales team is this engineer assuming?
• post-sales field engineer
• pre-sales engineer
• account manager
• network designer
12. Which two statements best describe the responsibilities of an account manager? (Choose two.)
• acts as the primary point of contact between the company and the client
• directs the sales teams and support personnel
• provides technical support to critical clients
• selects the equipment and technologies to be used for the client solution
• acts as the network design lead
13. What is the purpose of system-level acceptance testing?
• To develop an installation plan for the newly designed network
• to train end users and support personnel on the newly installed network
• to check that the newly installed network meets the business goals and design requirements
• to justify the financial investment required to implement the technology change
14. What is a purpose of establishing a network baseline?
• It provides a statistical average for network performance.
• It manages the performance of network devices.
• It creates a point of reference for future network evaluations.
• It checks the security configuration of network devices.
15. When should a network baseline be performed within the stages of the Cisco Lifecycle Services?
• Prepare Phase
• Plan Phase
• Design Phase
• Implement Phase
• Operate Phase
16. What are two benefits of using a top-down approach instead of a bottom-up approach to network design? (Choose two.)
• incorporates organizational requirements
• allows for a quick response to a design request
• requires less time up front to create a network design
• clarifies design goals from the perspective of applications and network solutions
• facilitates a design by using devices and technologies that are based on previous experience
17. Which software component is installed on network devices that are managed through SNMP?
• management agents
• management stations
• network management protocol
• Management Information Base (MIB)
18. A network engineer working for a contracting company is informed of a pre-bid meeting with a potential client. What purpose does the network engineer have for attending the pre-bid meeting?
• to submit request for proposal responses
• to discuss proposed installation and monitoring plans
• to perform system-level acceptance tests on the current network
• to clarify project scope and timelines not included in the original request for proposal
• to create a business case outlining reasons for financial investment in a network upgrade
19. A major corporation has decided to hire someone to upgrade their network infrastructure. A network consulting company wants the job. What document must the network consulting company obtain to learn about the business goals, the project scope, the requirements for the new network and the expected deliverables?
• Business Case
• Project Plan
• Request for Proposal
• Request for Comments
20. A corporation (client) wants a network upgrade and is putting out a request for services to various network consulting companies (contractors). A RFQ is required. Which statement is true concerning the RFQ?
• sent from the contractors to the client in response to a RFP
• sent from the client to the contractors along with the RFP to provide more specific technical details
• sent from the client to the contractors in place of a RFP when the technical specifications of a project are known
• sent from the contractors to the client outlining reasons for financial investments for the network upgrade
21. Which stage of the Cisco Lifecycle Services involves proactive management to identify and resolve issues before the organization is affected?
• Prepare Phase
• Plan Phase
• Design Phase
• Implement Phase
• Operate Phase
• Optimize Phase
22. Why is it important to prioritize business goals when developing network design?
• to ensure that the least expensive technologies are implemented first
• to simplify the configuration, administration, and monitoring of the newly installed network
• to anticipate the effects of changes and growth of the business
• to adhere to the best opportunities to contribute to the success of the business
23. Which two items help identify business goals and priorities before a new network project starts? (Choose two.)
• installation
• motivation
• profitability
• trustworthiness
• customer satisfaction
24. A network engineer working for ABC company is writing a response to an RFP for a network upgrade and must create an executive summary. Which statement describes the basic components of an executive summary?
• quick overview of the problem, the recommended solution, and the justification for ABC company doing the job
• detailed description of the solution, including but not limited to, timelines, turnover schedule, warranty information, and emergency recovery information
• detailed description of costs including, the cost of software and hardware components, licensing requirements, labor cost, and other applicable fees
• multiple page document containing additional information such as detailed lists of equipment required, diagrams, company background information, and insurance coverage
25. In a network management architecture, which statement best describes a management agent?
• communication protocol used between a management station and managed device
• standardized database that a device keeps about itself concerning network performance parameters
• host with the management application loaded that is used by the administrator to monitor and configure network devices
• software running on a managed device to collect network information and allow that device to be managed by a management station
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 8 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to add the command deny ip 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 any log to R3. After adding the command, the administrator verifies the change using the show access-list command. What sequence number does the new entry have?
• 0
• 10, and all other items are shifted down to the next sequence number
• 50
• 60
2.
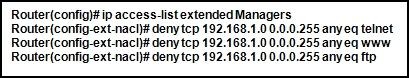
Refer to the exhibit. What happens if the network administrator issues the commands shown when an ACL called Managers already exists on the router?
• The new commands overwrite the current Managers ACL.
• The new commands are added to the end of the current Managers ACL.
• The new commands are added to the beginning of the current Managers ACL.
• An error appears stating that the ACL already exists.
3. Why are inbound ACLs more efficient for the router than outbound ACLs?
• Inbound ACLs deny packets before routing lookups are required.
• Inbound ACL operation requires less network bandwidth than outbound.
• Inbound ACLs permit or deny packets to LANs, which are typically more efficient than WANs.
• Inbound ACLs are applied to Ethernet interfaces, while outbound ACLs are applied to slower serial interfaces.
4.
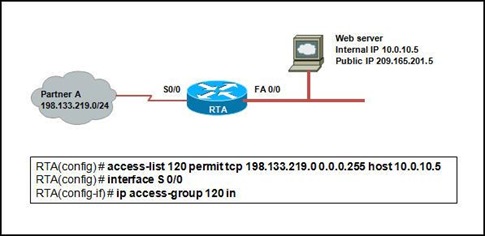
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator of a company needs to configure the router RTA to allow its business partner (Partner A) to access the web server located in the internal network. The web server is assigned a private IP address, and a static NAT is configured on the router for its public IP address. Finally, the administrator adds the ACL. However, Partner A is denied access to the web server. What is the cause of the problem?
• Port 80 should be specified in the ACL.
• The public IP address of the server, 209.165.201.5, should be specified as the destination.
• The ACL should be applied on the s0/0 outbound interface.
• The source address should be specified as 198.133.219.0 255.255.255.0 in the ACL.
5. ACL logging generates what type of syslog message?
• unstable network
• warning
• informational
• critical situation
6. Which two host addresses are included in the range specified by 172.16.31.64 0.0.0.31? (Choose two.)
• 172.16.31.64
• 172.16.31.77
• 172.16.31.78
• 172.16.31.95
• 172.16.31.96
7. Traffic from the 64.104.48.0 to 64.104.63.255 range must be denied access to the network. What wildcard mask would the network administrator configure in the access list to cover this range?
• 0.0.15.255
• 0.0.47.255
• 0.0.63.255
• 255.255.240.0
8. ACLs are used primarily to filter traffic. What are two additional uses of ACLs? (Choose two.)
• specifying source addresses for authentication
• specifying internal hosts for NAT
• identifying traffic for QoS
• reorganizing traffic into VLANs
• filtering VTP packets
9. What can an administrator do to ensure that ICMP DoS attacks from the outside are mitigated as much as possible, without hampering connectivity tests initiated from the inside out?
• Create an access list permitting only echo reply and destination unreachable packets from the outside.
• Create an access list denying all ICMP traffic coming from the outside.
• Permit ICMP traffic from only known external sources.
• Create an access list with the established keyword at the end of the line.
10. What effect does the command reload in 30 have when entered into a router?
• If a router process freezes, the router reloads automatically.
• If a packet from a denied source attempts to enter an interface where an ACL is applied, the router reloads in 30 minutes.
• If a remote connection lasts for longer than 30 minutes, the router forces the remote user off.
• A router automatically reloads in 30 minutes.
11.

Refer to the exhibit. The following commands were entered on RTB.
RTB(config)# access-list 4 deny 192.168.20.16 0.0.0.15
RTB(config)# access-list 4 permit any
RTB(config)# interface serial 0/0/0
RTB(config-if)# ip access-group 4 in
Which addresses do these commands block access to RTB?
• 192.168.20.17 to 192.168.20.31
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.31*
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.32
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.33
12.
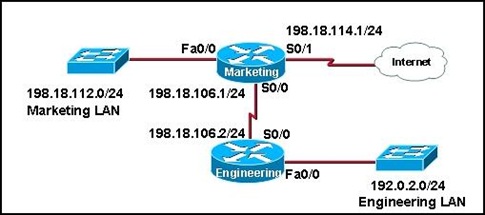
Refer to the exhibit. The new security policy for the company allows all IP traffic from the Engineering LAN to the Internet while only web traffic from the Marketing LAN is allowed to the Internet. Which ACL can be applied in the outbound direction of Serial 0/1 on the Marketing router to implement the new security policy?
• access-list 197 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 197 permit ip 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
• access-list 165 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 165 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
access-list 165 permit ip any any
• access-list 137 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 137 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
• access-list 89 permit 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 89 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
13. Which three statements are true concerning standard and extended ACLs? (Choose three.)
• Extended ACLs are usually placed so that all packets go through the network and are filtered at the destination.
• Standard ACLs are usually placed so that all packets go through the network and are filtered at the destination.
• Extended ACLs filter based on source address only, and must be placed near the destination if other traffic is to flow.
• Standard ACLs filter based on source address only, and must be placed near the destination if other traffic is to flow.
• Extended ACLs filter with many possible factors, and they allow only desired packets to pass through the network if placed near the source.
• Standard ACLs filter with many possible factors, and they allow only desired packets to pass through the network if placed near the source.
14.

Refer to the exhibit. Company policy for the network that is shown indicates the following guidelines:
1) All hosts on the 192.168.3.0/24 network, except host 192.168.3.77, should be able to reach the 192.168.2.0/24 network.
2) All hosts on the 192.168.3.0/24 network should be able to reach the 192.168.1.0/24 network.
3) All other traffic originating from the 192.168.3.0 network should be denied.
Which set of ACL statements meets the stated requirements when they are applied to the Fa0/0 interface of router R2 in the inbound direction?
• access-list 101 deny ip any any
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip any any
• access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
15.
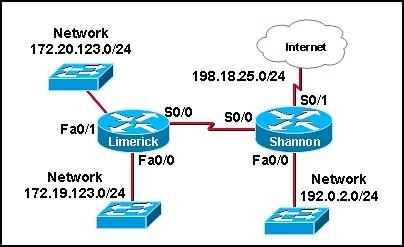
Hosts from the Limerick LAN are not allowed access to the Shannon LAN but should be able to access the Internet. Which set of commands will create a standard ACL that will apply to traffic on the Shannon router interface Fa0/0 implementing this security?
• access-list 42 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.255 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 42 permit any
• access-list 56 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 56 permit any
• access-list 61 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.0
access-list 61 permit any
• access-list 87 deny ip any 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 87 permit ip any
16.
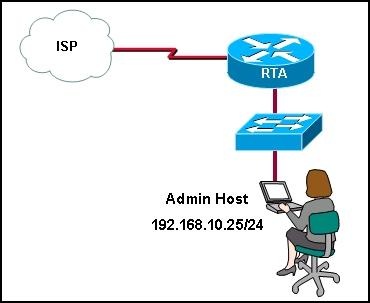
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure an access list that will allow the management host with an IP address of 192.168.10.25/24 to be the only host to remotely access and configure router RTA. All vty and enable passwords are configured on the router. Which group of commands will accomplish this task?
• Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any 192.168.10.25 0.0.0.0 eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip any any
Router(config)# int s0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
Router(config-if)# int fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ip access-group 101 in
• Router(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.10.25 eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 10 deny any
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)#access-group 10 in
• Router(config)# access-list 86 permit host 192.168.10.25
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)# access-class 86 in
• Router(config)# access-list 125 permit tcp 192.168.10.25 any eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 125 deny ip any any
Router(config)# int s0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 125 in
17. Which ACL permits host 10.220.158.10 access to the web server 192.168.3.244?
• access-list 101 permit tcp host 10.220.158.10 eq 80 host 192.168.3.224
• access-list 101 permit tcp 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 0.0.0.0 eq 80
• access-list 101 permit host 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 0.0.0.0 eq 80
• access-list 101 permit tcp 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 eq 80
18. Which wildcard mask would match the host range for the subnet 192.16.5.32 /27?
• 0.0.0.32
• 0.0.0.63
• 0.0.63.255
• 0.0.0.31
19. A security administrator wants to secure password exchanges on the vty lines on all routers in the enterprise. What option should be implemented to ensure that passwords are not sent in clear text across the public network?
• Use Telnet with an authentication server to ensure effective authentication.
• Apply an access list on the router interfaces to allow only authorized computers.
• Apply an access list on the vty line to allow only authorized computers.
• Use only Secure Shell (SSH) on the vty lines.
20.

Refer to the exhibit. An administrator notes a significant increase in the amount of traffic entering the network from the ISP. The administrator clears the access-list counters. After a few minutes, the administrator again checks the access-list table. What can be concluded from the most recent output shown?
• A small amount of HTTP trafic is an indication that the web server was not configured correctly.
• A larger amount of POP3 traffic (compared with SMTP traffic) indicates that there are more POP3 email clients than SMTP clients in the enterprise.
• A large amount of ICMP traffic is being denied at the interface, which can be an indication of a DoS attack.
• A larger amount of email traffic (compared with web traffic) is an indication that attackers mainly targeted the email server.
Rabu, 08 Desember 2010
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 5 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1. What three statements are true about routers that are configured for EIGRP? (Choose three.)
• They can support multiple routed protocols
• They can support only link-state protocols.
• They send their entire routing tables to neighboring routers.
• They send partial routing updates in response to topology changes.
• They send routing updates to all other routers in the network.
• They use hello packets to inform neighboring routers of their status.
2. Given the following commands:
Router(config)# router rip
Router(config-router)# network 192.31.7.0
What three conclusions can be determined based on the commands used on the router? (Choose three.)
• A link-state routing protocol is used.
• A distance vector routing protocol is used.
• Routing updates broadcast every 30 seconds.
• Routing updates broadcast every 90 seconds.
• Hop count is the only metric used for route selection.
• Bandwidth, load, delay, and reliability are metrics used for route selection.
3. What is indicated when an EIGRP route is in the passive state?
• The route has the highest path cost of all routes to that destination network.
• The route must be confirmed by neighboring routers before it is put in the active state.
• The route is a feasible successor and will be used if the active route fails.
• There is no activity on the route to that network.
• The route is viable and can be used to forward traffic.
4. What two problems may occur if the EIGRP default bandwidth for a serial link is higher than the actual bandwidth? (Choose two.)
• Routing updates will arrive too quickly for receiving routers to process.
• The port IP address will be rejected by the routing protocol.
• Suboptimal paths will be selected.
• The port protocol will return to the HDLC default.
• VLSM support will be disabled.
• Network convergence may be affected.
5. What is the default administrative distance for EIGRP internal routes?
• 70
• 90
• 100
• 110
• 120
• 255
6. A network administrator issues the command show ip route and sees this line of output:
192.168.3.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:05, Serial0/0
What two pieces of information can be obtained from the output? (Choose two.)
• RIP is the routing protocol configured.
• This is a static route to network 192.168.3.0.
• The metric for this route is 2.
• The next periodic update is in 5 seconds.
• The autonomous system number is 120.
7.
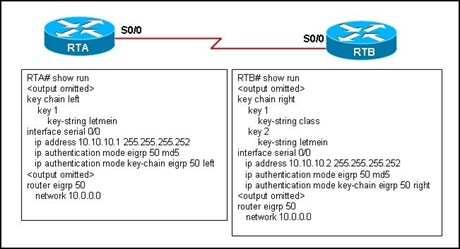
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the EIGRP authentication configuration?
• RTA and RTB will accept updates from each other.
• RTA and RTB will not accept updates from each other because key 1 on RTB does not match RTA.
• RTA and RTB will not accept updates from each other because the key chain names do not match.
• The ip authentication mode AS does not match the locally configured AS.
8. Which Layer 4 protocol does EIGRP use to provide reliability for the transmission of routing information?
• DUAL
• IP
• PDM
• RTP
• TCP
• UDP
9.

Refer to the exhibit. Routers RTR-1 and RTR-3 are completely configured. The administrator needs to configure the routing protocol on router RTR-2 so that communication occurs throughout the network. Which group of commands will successfully configure EIGRP on RTR-2?
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.4 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.128 0.0.0.192 no-summary
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.192 0.0.0.192 area 0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.4 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.128 0.0.0.192
10. What prevents RIPv1 updates from being correctly advertised?
• an increase in network load
• the use of variable length subnet masks
• the use of multiple Layer 3 networks on the same router
• a variation in connection speeds on the links to a destination
• a mismatch between the configured bandwidth and the actual bandwidth of a link
11. What does a router that is running RIP use to determine the best path to take when forwarding data?
• the host portion of the network address
• the speed of network convergence
• the calculated metric for the destination network
• the number of broadcasts occurring on an interface
• the number of errors occurring on an interface
12. What is the purpose of the network command when RIP is being configured as the routing protocol?
• It identifies the networks connected to the neighboring router.
• It restricts networks from being used for static routes.
• It identifies all of the destination networks that the router is allowed to install in its routing table.
• It identifies the directly connected networks that will be included in the RIP routing updates.
13. How do EIGRP routers establish and maintain neighbor relationships?
• by exchanging neighbor tables with directly attached routers
• by comparing known routes to information received in updates
• by exchanging hello packets with neighboring routers
• by dynamically learning new routes from neighbors
• by exchanging routing tables with directly attached routers
14.
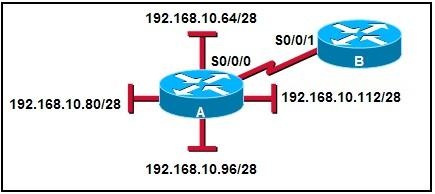
Refer to the exhibit. Routers A and B have EIGRP configured and automatic summarization has been disabled on both routers. Which router command will summarize the attached routes?
• ip area-range eigrp 1 192.168.10.80 255.255.255.224
• ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192
• ip summary-address 192.168.10.80 0.0.0.31
• ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63
• ip area-range eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.224
15. How often does RIPv2 send routing table updates, by default?
• every 30 seconds
• every 45 seconds
• every 60 seconds
• every 90 seconds
16.
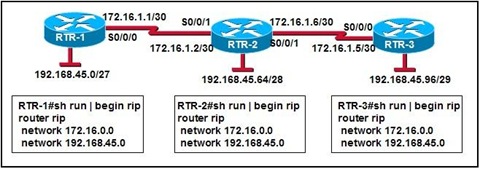
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a routing problem. When the show ip route command is entered on RTR-1, only the serial link between RTR-2 and RTR-3 has been learned from the RIP routing protocol. What are two issues? (Choose two.)
• RIPv1 is a classful routing protocol.
• RIPv1 does not support subnetting.
• The Ethernet networks on RTR-2 and RTR-3 were not entered correctly in the network statements on these routers.
• RIPv1 does not support VLSM.
• RIPv1 is a classless routing protocol.
17. What two statements are correct regarding EIGRP authentication? (Choose two.)
• EIGRP authentication uses the MD5 algorithm.
• EIGRP authentication uses a pre-shared key.
• EIGRP authentication requires that both routers have the same key chain name.
• EIGRP authentication uses varying levels of WEP to encrypt data exchanged between routers.
• EIGRP authentication can be configured on one router and updates from this router are protected; whereas a neighbor router can be without the authentication configuration and its updates are unprotected.
18. When should EIGRP automatic summarization be turned off?
• when a router has not discovered a neighbor within three minutes
• when a router has more than three active interfaces
• when a network contains discontiguous network addresses
• when a router has less than five active interfaces
• when a network addressing scheme uses VLSM
19. What is the maximum number of hops that RIP will attempt before it considers the destination unreachable?
• 14 hops
• 15 hops
• 16 hops
• 17 hops
20. What two statements are true regarding EIGRP tables? (Choose two.)
• A feasible successor route can be found in the topology table.
• A successor route can only be found in the routing table.
• The topology table shows whether a route is in the passive or active state.
• The routing table shows the amount of time elapsed since a router adjacency was formed.
• The neighbor table shows all adjacent Cisco devices.
• Administrative distance is shown as a column in the neighbor table.
21.
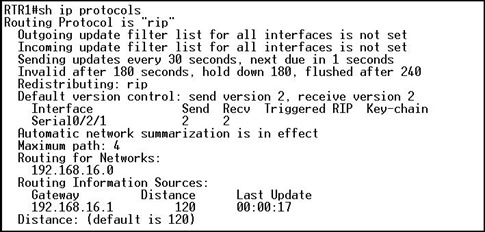
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the output from the show ip protocols command?
• RIPv2 is configured on this router.
• Auto summarization has been disabled.
• The next routing update is due in 17 seconds.
• 192.168.16.1 is the address configured on the local router
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 4 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1
2
4
6
8
16
2 When running NAT, what is the purpose of address overloading?
limit the number of hosts that can connect to the WAN
allow multiple inside addresses to share a single global address
force hosts to wait for an available address
allow an outside host to share inside global addresses
3 What two advantages does CIDR provide to a network? (Choose two.)
reduced routing table size
dynamic address assignment
automatic route redistribution
reduced routing update traffic
automatic summarization at classful boundaries
4 How does a router keep track of which inside local address is used when NAT overload is configured?
The router adds an additional bit to the source IP address and maintains a separate table.
The router modifies the QoS field.
The router uses TCP or UDP port numbers.
The router uses a manual entry that is created and maintained in the database of the router.
5 What is a characteristic of a classful routing protocol on the network?
All subnets are seen by all routers.
CIDR addresses are advertised.
A subnet can be further subnetted down and advertised correctly.
Updates received by a router in a different major network have the default mask applied.
6 Refer to the exhibit. Which address is an inside global address?
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.2
198.18.1.55
64.100.0.1
7 Refer to the exhibit. All networks that are shown have a /24 prefix. Assuming that all routes have been discovered by all routers in the network, which address will successfully summarize only the networks that are shown?
192.168.8.0/21
192.168.8.0/24
192.168.16.0/20
192.168.16.0/21
192.168.16.0/24
8 What is the CIDR prefix designation that summarizes the entire reserved Class B RFC 1918 internal address range?
/4
/8
/12
/16
/20
9 Which NAT term refers to the IP address of your inside host as it appears to the outside network?
inside global IP address
outside global IP address
inside local IP address
outside local IP address
10 A network administrator is asked to design a new addressing scheme for a corporate network. Presently, there are 500 users at the head office, 200 users at sales, 425 at manufacturing, and 50 at the research site. Which statement defines the correct VLSM addressing map with minimal waste using the 172.16.0.0/16 network?
172.16.0.0/20 head office
172.16.1.0/21 manufacturing
172.16.1.0/22 sales
172.16.3.0/26 research
172.16.48.0/19 head office
172.16.16.0/20 manufacturing
172.16.48.128 sales
172.16.48.0/26 research
172.16.2.0/23 head office
172.16.4.0/23 manufacturing
172.16.6.0/24 sales
172.16.7.0/26 research
172.16.2.0/22 head office
172.16.3.0/23 manufacturing
172.16.4.0/26 sales
172.16.4.128/25 research
11 A company using a Class B IP addressing scheme needs as many as 100 subnetworks. Assuming that variable length subnetting is not used and all subnets require at least 300 hosts, what subnet mask is appropriate to use?
255.255.0.0
255.255.240.0
255.255.254.0
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.192
12 Host A in the exhibit is assigned the IP address 10.118.197.55/20. How many more network devices can be added to this same subnetwork?
253
509
1021
2045
4093
13 Refer to the exhibit. RIP version 2 is configured as the network routing protocol and all of the default parameters remain the same. Which update is sent from R2 to R3 about the 10.16.1.0/24 network connected to R1?
10.16.0.0/16
10.0.0.0/24
10.0.0.0/8
10.16.1.0/24
14 What range of networks are summarized by the address and mask, 192.168.32.0/19?
192.168.0.0/24 - 192.168.32.0/24
192.168.0.0/24 - 192.168.31.0/24
192.168.32.0/24 – 192.168.64.0/24
192.168.32.0/24 – 192.168.63.0/24
15 Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output of the show ip nat translations command, which kind of address translation is in effect on this router?
static
public
overload
private
16 How many addresses will be available for dynamic NAT translation when a router is configured with the following commands?
Router(config)#ip nat pool TAME 209.165.201.23 209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 9 pool TAME
7
8
9
10
24
31
17 Refer to the exhibit. Which two IP addresses could be assigned to the hosts that are shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
192.168.65.31
192.168.65.32
192.168.65.35
192.168.65.60
192.168.65.63
192.168.65.64
18 What are the network and broadcast addresses for host 192.168.100.130/27? (Choose two.)
network 192.168.100.0
network 192.168.100.128
network 192.168.100.130
broadcast 192.168.100.157
broadcast 192.168.100.159
broadcast 192.168.100.255
19 Refer to the exhibit. Which two are valid VLSM network addresses for the serial link between Router1 and Router2? (Choose two.)
192.168.1.4/30
192.168.1.8/30
192.168.1.90/30
192.168.1.101/30
192.168.1.190/30
20 When configuring NAT on a Cisco router, what is the inside local IP address?
the IP address of an inside host as it appears to the outside network
the IP address of an outside host as it appears to the inside network
the IP address of an inside host as it appears to the inside network
the configured IP address assigned to a host in the outside network
Langganan:
Postingan (Atom)
